Google Shopping Optimization: Key Highlights
-
Campaign structure shapes efficiency: Well-segmented campaigns improve budgeting, speed of iteration and ROAS.
-
Top products deserve targeted spend: Using high-converting SKUs boosts margin contribution and reduces wasted impressions.
-
Feed quality defines visibility: Clean, accurate data ensures eligibility and ranking, directly impacting your share of high-intent search results.
Someone’s next big purchase might already be sitting in their search bar, half-typed and fueled by curiosity and intent.
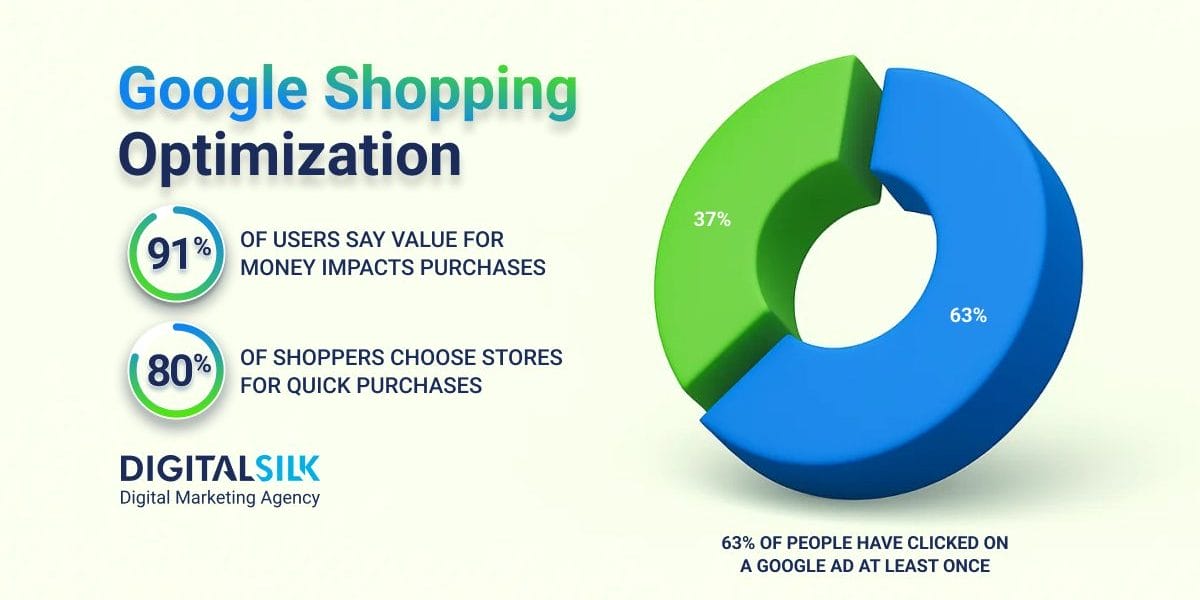
With 15% of users turning to search engines for shopping inspiration, search engines rank third among consumers as a leading source of inspiration when shopping online.
Shopping ads perform best when the feed is built with intention, the structure supports scale and the data behind it keeps pace with real buyer behavior.
In this post, we’ll explore 10 Google shopping optimization strategies with useful examples that help you get in front of ready-to-buy shoppers before your competitors do.
10 Best Google Shopping Optimization Strategies
63% of people have clicked on a Google Ad at some point, which speaks volumes about how deeply these paid advertising formats are woven into the buying process.
Shopping ads in particular play a distinct role as they meet intent with product, often in real time and at scale.
The Google shopping optimization tips below focus on structure, targeting and data flow, offering practical ways to improve how your campaigns show up and convert.
1. Prioritize Targeting And Segmentation
29.7% of U.S. consumers use search engines to discover new products and over half of them turn to Google, naming it the most influential advertising format.
That level of reach only delivers if your campaigns are built around audiences defined by real behavior, location and buying signals.
Effective shopping campaigns start with a clear understanding of who your strongest buyers are, what influences their decisions and how you can address their pain points.
Tailoring your product listings to high-performing segments increases relevance and helps your campaigns stay closely aligned with how real customers search, browse and buy.
To build a campaign that reflects those insights, focus on the following:
- Segment by geography, age, gender or device type as a foundation for more tailored targeting
- Use regional segmentation to align ads with fulfillment capabilities and avoid promoting products in areas where delivery isn’t possible
- Review your product catalog with demand and market fit in mind before launching any campaigns
- Use tools like Google Trends, keyword platforms, social listening and competitive research to understand what your audience is searching for
- Identify gaps in both consumer demand and competitor offerings where your products can stand out
2. Determine Campaign Structure
How you structure a Google shopping campaign directly shapes your ability to manage spend, track performance and respond to shifts in demand in a timely manner.
A well-organized setup makes it easier to align product visibility with business goals and uncover where adjustments can drive meaningful results.
This is especially important in the U.S., which has the highest global average cost per click in marketing and advertising at $7.66, which makes a well-structured approach to Google shopping campaign optimization a priority from the start.
When creating a standard Shopping campaign, begin with one group that includes all products, then segment using data feed attributes that reflect how you measure performance, including category, brand, product type, item ID, condition or custom labels.
Here’s how to structure it:
- Create an initial product group that includes all products
- Choose a relevant attribute from your feed to segment the group
- Select attribute values to generate new product groups
- Further subdivide each group using additional attributes
- Build a hierarchy such as Category > Product Type > Item ID
- Use the automatically created “Everything else” group to manage unsegmented products with separate settings
Performance Max Vs. Standard Shopping: Choosing Your 2025 Strategy
The dynamics of Google Shopping have changed significantly, with Performance Max campaigns now dominating Shopping ad spend.
It’s crucial to understand when and how to utilize each campaign type to maximize your results in 2025.
When you can use Performance Max:
- New product launches: AI optimization works best with fresh data
- Large product catalogs: Where manual management becomes impractical
- Omnichannel goals: When you want to appear across YouTube, Discovery, Gmail and Search simultaneously
- Limited time for optimization: Google’s automation handles bid adjustments and audience targeting
When you can use Standard Shopping:
- Precise control needs: When you need granular bid management at the product group level
- Niche or specialized products: Where Google’s AI may struggle with audience identification
- Budget constraints: When you need exact control over spend allocation
- Testing and learning phases: Try out the other model before scaling to Performance Max
When to take the hybrid strategy approach and use both:
- High Priority Standard Shopping: Target your best-performing products with precise bids
- Medium Priority Performance Max: Capture broader audience reach with AI optimization
- Low Priority Standard Shopping: Catch-all campaign for remaining inventory
3. Optimize Product Titles And Descriptions
80% of shoppers say getting their shopping done quickly matters when deciding where to buy, which makes clarity in product listings more than a formatting task.
With Google shopping product title optimization, the focus is on helping shoppers instantly understand what you’re offering and helping Google match your products to relevant searches.
Product titles are the primary input Google uses to connect your items to user intent.
Since Shopping ads don’t allow for custom headlines or creative copy, the title is your headline and your targeting signal that reflects the way your customers actually search.
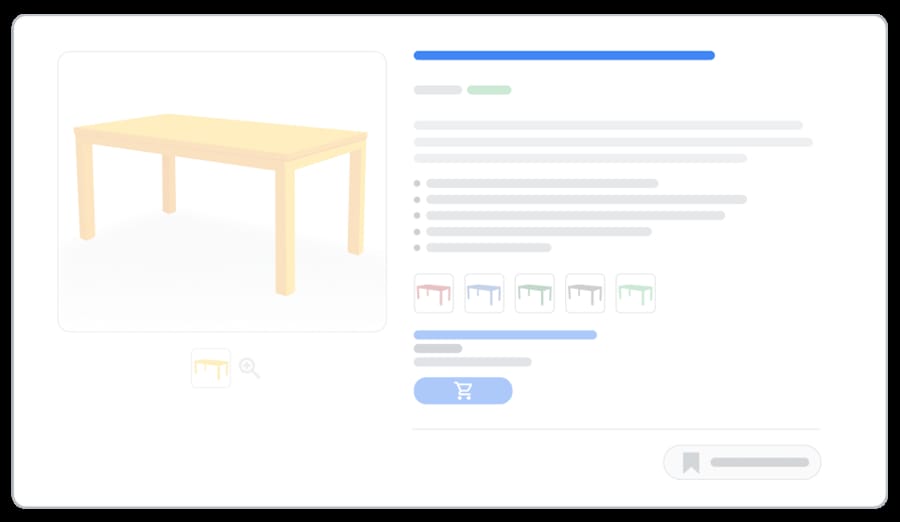
Use the following Google shopping title optimization strategies:
- Use up to 150 characters, with the most important information in the first 70
- Include brand, product type, size, color, material or any other attributes that help differentiate variants
- Add variant details like age group or flavor directly into the title if they help clarify the product
- Make sure titles align with the product shown on your landing page
- Avoid promotional text, symbols, extra spacing or all caps formatting
- Use the title attribute for manually written titles or the structured_title attribute with the correct sub-attributes for AI-generated content
Descriptions are where you expand on the details and improve how your products are found:
- Add relevant secondary keywords that didn’t fit into the title
- Describe key features, use cases or benefits that matter to your target audience
- Keep messaging aligned with the landing page to avoid inconsistencies
- Use clear, grammatically correct language without filler or overstatement
- Include variant-specific details where applicable for consistency across listings
Below are some practical examples for Google Shopping product listing optimization:
| Product | Bad Title | Optimized Title |
| Running Shoes | “Nike Zoom” | “Nike Zoom X Vaporfly Next% Men’s Running Shoes – Size 10 -Blue” |
| Coffee Maker | “Espresso Machine” | “Breville Barista Express Espresso Machine with Grinder – Stainless Steel” |
| Laptop | “HP Laptop” | “HP Pavilion 15.6″ Laptop, Intel i7, 16GB RAM, 512 GB SSD – Silver” |
4. Use High-Quality Product Images And Videos
Product visuals are often the first point of contact between your brand and a potential customer.
They influence not just perception but also performance, determining how your listings are ranked, displayed and clicked.
The human brain processes images up to 60,000 times faster than text, which makes visual accuracy a key factor in effective Google shopping feed optimization.
Even a fully compliant product feed will underperform if the images are unclear, misleading or improperly formatted.
You can take it a step further by using visuals that reflect real-world use. Listings with 3D images, for example, receive 50% more engagement than static ones.
This added dimension creates a more immersive experience and helps shoppers connect with your product.
For teams optimizing at scale, image compliance and visual appeal go hand in hand.
To meet Google’s image quality and compliance standards:
- Use high-resolution images with a minimum of 100 x 100 pixels for most items and 250 x 250 px for apparel
- Frame the product to take up between 75% and 90% of the image space
- Use a solid white or transparent background unless a clean lifestyle image adds context
- Avoid overlays, promotional text, watermarks, logos or placeholder graphics
- Submit a unique image for each product variant that accurately shows distinguishing details
Here’s an example of how your Google shopping feed optimization should look like:
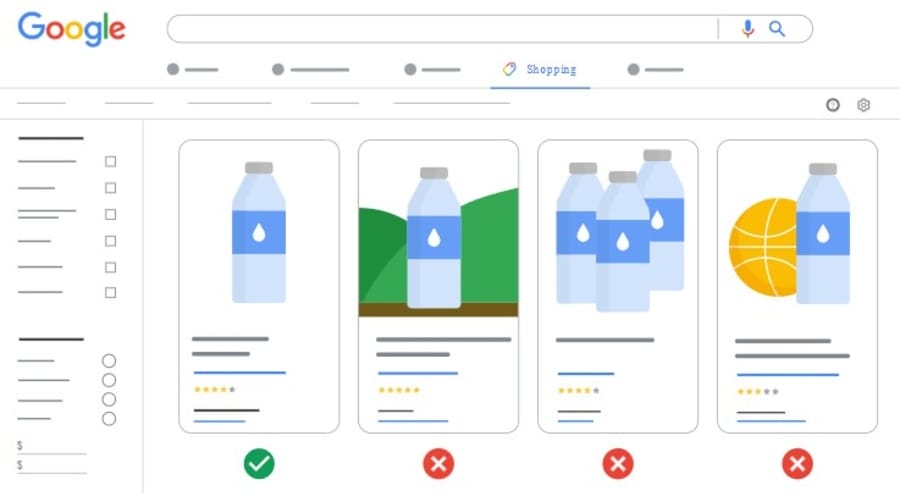
To keep your visuals working within the feed:
- Use a stable image URL that doesn’t change unless the image itself is replaced
- Make sure image URLs are crawlable and follow standard formatting with no dynamic strings
- If replacing an image, submit a new URL to prompt faster recrawling
- Add additional views or lifestyle angles using the additional_image_link attribute
- Consider testing new product visuals using Search Console’s URL Inspection tool before publishing at scale
When visuals meet both technical standards and buyer expectations, your products load faster, look better and convert more consistently.
5. Divide Products Into Different Ad Groups
Ad group segmentation gives your team more control over how products are organized, displayed and measured.
It allows you to separate product categories, prioritize high-margin items and fine-tune performance without unnecessary overlap.
This structure also simplifies reporting and makes campaign adjustments more actionable across large catalogs.
To organize variant products and improve how they appear in Shopping ads:
- Use the item_group_id attribute to group variants of a single product that differ by size, color, material, pattern, age group or gender
- Assign the same group ID to all related variants and ensure each one has a unique product ID
- Provide consistent variant attributes across all products in the same group to avoid disapproval
- Each variant should link to a unique landing page that reflects its specific details
- Use the parent SKU as the group ID when appropriate, but do not submit the parent product as a standalone item
- Keep group IDs consistent over time and avoid reusing them for different products
For example, a red Google T-shirt in size small and a blue one in size medium would each have unique product IDs, titles and URLs, but share the same group ID to signal that they are part of the same product set:

6. Implement Negative Keywords
Every product shown in a Shopping campaign comes with a cost, whether or not the click leads to a purchase.
Since Google Shopping doesn’t give you control over which exact keywords trigger your ads, your products can appear in searches that have little to do with what you’re actually selling.
Negative keywords help you manage that risk by excluding queries that are unlikely to convert, keeping your spend focused and your campaign cleaner.
Even if you target exact match keywords, as 42% of marketers consistently do, your results may still fall short without a strategy for excluding irrelevant terms.
There are two ways to apply negative keywords to your Google shopping product feed optimization:
- Campaign-level negatives exclude broad, irrelevant queries across your entire campaign. These are usually terms that don’t belong anywhere in your product catalog.
- Ad group-level negatives allow for more nuanced control by blocking certain queries in one group while keeping them available in others. This helps reduce overlap and keeps product targeting more precise.
To put negative keywords into practice:
- Review search term reports regularly to find irrelevant queries that trigger impressions or clicks
- Add filters using exact match for specific terms, phrase match for common expressions or broad match with multiple variations
- Include singular, plural and related synonyms when applicable, e.g. cup, glass, glasses
- Be consistent with variant exclusions if your product line doesn’t cover certain sizes, colors or formats
For example, if you offer green, yellow and pink t-shirts, but not black, adding “black” as a negative keyword ensures your ads don’t show up for irrelevant queries.
7. Highlight Top Performers
Not all products contribute equally to performance. Some convert reliably, generate consistent revenue and offer stronger margins than the rest.
Prioritizing these items in your Google Shopping campaigns helps focus your budget where it delivers the most value.
Globally, 91% of consumers say good value for money influences their purchase decisions, and that number rises to 93% in the U.S.
Featuring your top performers supports this expectation and reinforces relevance with high-intent shoppers.
Use performance data to pinpoint which products drive results. Filter by item ID, product type or brand and track conversions, cost per conversion and return on ad spend.
A T-shirt with 100 clicks and no sales may be a weak performer, while a lower-traffic item with a high conversion rate could justify a more aggressive bid.
Once identified, group high-performing items into their own product targets. Raise bids where performance justifies the cost and reduce or exclude items with poor return.
This includes products with high traffic but no conversions, as well as those where the cost to convert exceeds your margin.
You can also exclude products with limited appeal, such as out-of-stock items or unusual sizes that rarely convert.
Google will automatically pause ads for items marked as sold out, but your feed still needs to reflect inventory changes in real time.
8. Set Relevant Bids And Budgets
In 2024, 72% of global marketers increased their ad budgets to keep pace with rising competition.
But allocating more spend without adjusting where and how it’s used can lead to diminishing returns.
In Shopping campaigns, performance varies widely based on timing, location, device and product category.
Bid adjustments allow you to direct spend where it’s more likely to convert.
Instead of relying on a flat structure, use performance signals to refine how your budget is distributed across key variables.
Focus your Google ads shopping optimization on these three areas:
- Location: Geographic performance is rarely uniform. Increase bids in regions with strong conversion rates, higher margins or strategic sales goals. Decrease bids where traffic underperforms or fulfillment costs cut into profitability.
- Device: If desktop users consistently complete purchases while mobile visitors browse but rarely convert, your device-level bidding should reflect that. Use historical data to prioritize devices that produce the most efficient outcomes.
- Schedule: Certain hours or days may drive more efficient conversions. Use reporting to identify when your cost per conversion is lowest and increase bids during those windows. Pull back during times that generate clicks without meaningful return.
9. Review Google Merchant Center
Google Merchant Center gives your direct visibility into how product data is being interpreted and used across Shopping placements.
It’s where feed quality, eligibility and product performance intersect, making it a core part of any optimization workflow.
Product accuracy is only part of the equation. Merchant Center helps you surface deeper insights, like which items are disapproved, what values are missing and where formatting issues may be blocking visibility.
These are the kinds of problems that don’t always show up in performance data but can quietly limit reach and spend efficiency.
Structured data from your site can enhance this further, giving Google more context to interpret your listings across both paid and organic placements.
10. Track And Analyze Ad Performance
Shopping campaigns perform best when changes are tracked deliberately and reviewed with enough data to reveal clear trends.
With 88% of marketers naming revenue as their primary key performance indicator (KPI), every adjustment should be evaluated through the lens of financial return.
After making a change to your campaign, allow at least one to two weeks before assessing its impact.
Use a comparison window, such as the last 7 or 14 days against the previous period, to see how key metrics are shifting.
Focus on metrics that provide a direct view into Google shopping optimization performance:
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): Measures how much revenue you earn for every dollar spent. If ROAS drops, assess whether bids are too high, products are underperforming or conversion rates have slowed.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Shows how often people click your ad after seeing it. A low rate may indicate weak product titles, poor images or irrelevant queries.
- Impression Share: Reflects how often your ads are shown out of the total number of opportunities. Drops can result from budget constraints or increased competition.
- Conversion Rate: Tracks how many clicks turn into completed purchases. A strong click-through rate with low conversions may point to issues with landing pages, pricing or stock availability.
- Search Lost Impression Share (Budget or Rank): Helps you see if you’re losing visibility due to limited budget or low bids. Budget-related losses may require reallocation, while rank-based losses may signal the need for higher bids or better feed quality.
- Cost-Per-Click (CPC) and Click-Through Rate (CTR) Benchmarks
Comparing your performance to industry benchmarks helps frame internal discussions and spot areas that may need further attention. - Bounce Rate: Indicates whether users leave your site quickly after clicking. A high bounce rate may reflect poor landing page alignment, slow site performance or mobile usability issues.
Why Google Shopping Optimization Strategies Matter
Without a clear strategy, it becomes difficult to control spend, scale results or understand what’s actually driving performance.
Here’s what strong Google shopping ads optimization can deliver:
- Better ROAS: With the average cost per lead on Google Ads reaching $70.11 in 2025, even minor inefficiencies can add up quickly. Optimization ensures your budget is focused on product listings and queries that convert.
- Improved campaign visibility: Well-maintained product data increases eligibility and search relevance. Optimization ensures your listings appear where they’re most likely to influence purchase decisions. Since 19% of product searches on Google lead to clicks on Shopping listings, strong visibility in these results directly impacts performance.
- More effective bid distribution: Performance varies across device types, times of day and geographic regions. Adjusting bids based on these signals helps direct spend where it has the most impact.
- Reduced spend on low-value clicks: Negative keywords and product exclusions help filter out queries that drive traffic but not revenue. This keeps your budget aligned with high-intent shoppers.
- Faster insight into what’s working: Ongoing review of item-level performance shows which products are delivering and which ones are holding the campaign back. Optimization gives you a framework to act on those findings.
How To Scale High-Performing Shopping Campaigns
Once your campaigns are generating consistent returns, scaling becomes the next opportunity.
The goal is to expand without compromising efficiency, which requires a disciplined, test-driven approach.
Here are three ways to scale with control:
- Expand gradually and monitor closely: Raise budgets in small increments of 10 to 20 percent and check performance daily. Replicate high-performing campaigns and tailor them to new regions or audience segments to build on what’s proven.
- Balance automation with oversight: Automate tasks like bidding and scheduling where possible but continue to review key metrics such as cost-per-click and feed status. Keep a record of all adjustments so results can be traced and explained.
- Test with purpose: Try lookalike audiences, similar product groupings or updated creative elements like new images or time-based bids. Keep test budgets limited until results show consistent performance.
Optimize Google Shopping Campaigns With Digital Silk
Effective Google Shopping campaigns are shaped by clear data, thoughtful adjustments and a steady focus on what influences buyer decisions.
Long-term growth comes from improving what already works and making every change count.
Digital Silk follows this approach to deliver scalable, performance-focused campaigns that connect products with the right shoppers at the right time.
As a professional digital marketing agency, our services include:
- SEO services
- Social media marketing
- Paid advertising
- Branding solutions
- Custom web design
- Custom web development
For each project, our dedicated specialists take on a proactive yet consultative approach, ensuring transparent communication and tangible results.
Contact our team, call us at (800) 206-9413 or fill in the Request a Quote form below to schedule a consultation.
"*" indicates required fields