Technical SEO: Key Highlights
-
Technical SEO powers rankings: It enables search engines to crawl, understand and index your content, directly impacting rankings and visibility.
-
Audit with purpose: Prioritize the technical gaps that block search performance instead of chasing minor issues.
-
Let search engines do their job: Clean code, fast load times and secure pages remove the barriers to discovery.
Technical SEO determines whether search engines can properly access, understand and rank your website.
In 2025, 19.1% of SEO specialists cite low confidence in deep technical SEO knowledge, the most common gap in the field.
Without clear priorities, even experienced teams waste time fixing the wrong things.
In this post, we’ll cover the best practices you need to follow and share a free technical SEO checklist and template to help them put those into action where it counts.
Step 1. Conduct A Technical SEO Audit
In 2024, 91% of companies saw SEO drive better website performance and stronger marketing results, yet the technical foundation behind those wins is often neglected.
A technical SEO site audit examines how search engines crawl, index and interpret your website’s structure, identifying the barriers that prevent pages from ranking efficiently.
Without this visibility, teams risk spending time on surface-level fixes while deeper technical issues continue to limit growth.
Start by defining clear objectives that align with your business model, so the audit focuses on areas that impact performance.
Then establish key performance indicators (KPIs) like index coverage and crawl efficiency to create a measurable baseline.
This gives your teams a structured way to track improvements and turn technical SEO from a one-time project into ongoing operational clarity.
You can use the following tools to perform a comprehensive technical audit for SEO:
- Site Crawlers: Tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb simulate how search engines crawl your site, uncovering broken links, redirect chains, duplicate content and orphan pages.
- Google Search Console: Direct insight from Search Console on indexing status, Core Web Vitals, crawl errors and page-level issues that prevent proper discovery and ranking.
- Server Log Analysis: Helps you understand how often search engines crawl your pages and where crawl budget may be wasted on irrelevant or low-value URLs.
- Page Speed and Rendering Tools: Lighthouse, PageSpeed Insights and GTMetrix highlight performance bottlenecks and rendering issues that slow down load times or block search engines from seeing key content.
- Analytics Platforms: Tools like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) connect technical issues with user behavior, showing where slow load times or broken features reduce engagement and conversions.
- On-Page SEO Auditors: Platforms like Ahrefs’ Site Audit or SEMRush Site Audit provide additional checks for crawl waste, duplicate metadata and thin content that hurt efficiency.
Step 2. Improve Site Structure And Navigation
Site architecture and navigation decide how easily search engines and users reach your most important content.
If your structure is confusing or inconsistent, even the best pages will be missed.
38% of people say that page layout and navigational links shape their first impressions of a website, so this strategy directly impacts how people engage with your brand.
A clear site structure allows teams to grow the site without adding complexity and gives search engines a straightforward path to your key pages.
Below are five areas any technical SEO expert should audit and improve:
1. Optimize URL Structure
A well-structured URL reflects the content of the page and the section it belongs to.
This helps both users and search engines understand what the page is about before they visit it.
Some best practices to follow in your SEO strategy include:
- Be descriptive: Use keywords that clearly describe the page. Example: example.com/seo-tips instead of example.com/page-671.
- Keep it short: Shorter URLs are easier to read, share and remember. Example: example.com/about instead of example.com/how-our-company-started-our-journey-page-update.
- Match your site hierarchy: Let your URLs reflect your content structure. Example: example.com/blog/seo-tips helps users and search engines understand this is part of the blog section.
- Use hyphens, not underscores: Hyphens act as word separators for search engines, improving readability and indexation. Example: example.com/seo-tips vs. example.com/seo_tips
- Avoid special characters and capital letters: Lowercase-only URLs without characters like ?, &, %, = can minimize confusion and help avoid link-breaking issues. Example: example.com/contact-us as opposed to example.com/Contact%20Us?id=5
- Include primary keywords: Focused, relevant terms help both users and search engines understand the page’s topic. Example: example.com/digital-marketing-guide instead of example.com/article-1234
- Avoid dates unless necessary: Adding dates can make the content appear outdated quickly. Use only if timeliness is crucial (like news or events). Example: example.com/black-friday-deals
- Don’t keyword-stuff: This outdated practice can harm your SEO strategy and can signal spam to search engines. Use keywords naturally and with purpose. Example: example.com/seo-tips not example.com/seo-seo-optimization-seo-tips
Clean, structured URLs also simplify future site maintenance and scaling, reducing the risk of crawl inefficiencies.
2. Include Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs give users a clear sense of where they are on your site and make it easier to move between pages without restarting from the homepage.
They also provide search engines with additional context about how your pages fit together.
At Digital Silk, we’ve implemented breadcrumbs in the Digital Trends section to help users explore related topics and navigate between categories smoothly.
Well-placed breadcrumbs are particularly helpful on larger sites with deep page hierarchies, improving both user experience and crawl efficiency.
3. Limit Click Depth
Pages buried too deeply in your site structure often remain undiscovered by users and crawlers.
56% of customers expect to find what they are looking for in three clicks or less, meaning slow or complicated navigation directly undermines their experience and trust.
Start by reviewing your main navigation and homepage links to surface key categories, best-selling products or high-priority resources.
For example, an eCommerce site should link directly to popular product categories, not hide them several layers down.
Strengthen this by building meaningful internal links between related pages.
For instance, a B2B services page on “technical SEO audits” should link to related content like “Core Web Vitals optimization” or “structured data implementation,” helping users and search engines navigate between connected topics.
You can use SEMrush’s Internal Linking report to quickly identify pages that sit too deep in the structure and reduce unnecessary layers and make important pages easier to find and crawl.
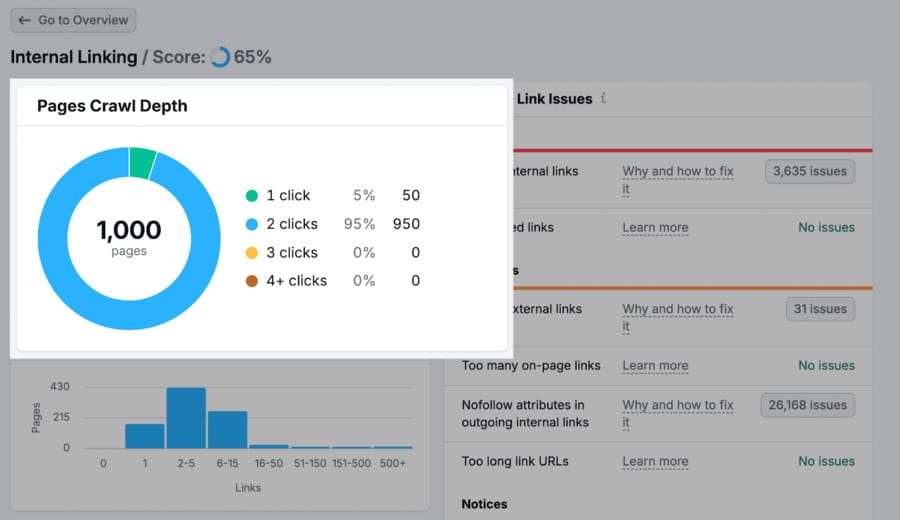
4. Determine Orphan Pages
Orphan pages have no internal links pointing to them, so they’re invisible to both users and search engines unless they are discovered through your sitemap or external backlinks.
You can use Ahrefs’ Site Audit to surface orphaned pages under the Links > Issues > Orphan page report.
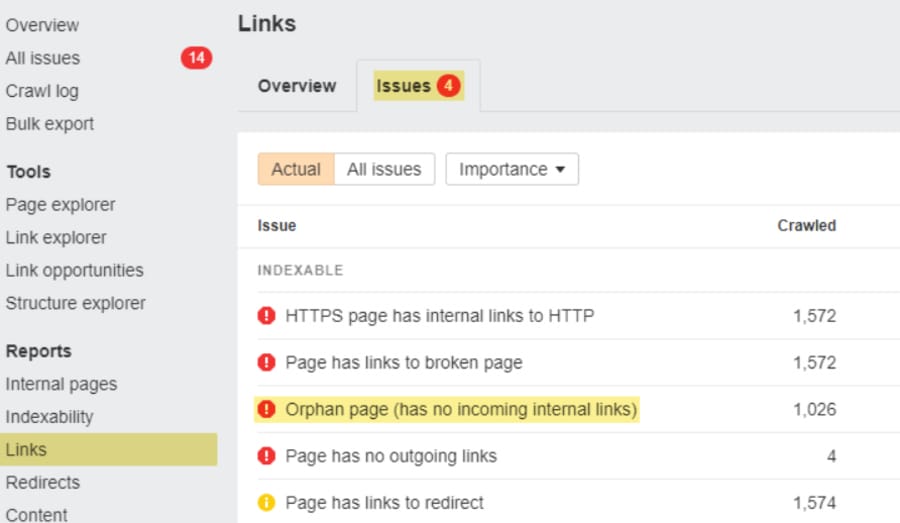
Start with indexable pages that still drive some organic traffic and add internal links to increase visibility and performance quickly.
Without internal links, these pages don’t pass or receive link value, reducing their ability to rank and driving crawl inefficiency.
Reconnect them to the most relevant categories or related content to bring them back into your site’s structure.
Step 3. Identify Crawlability And Indexation Issues
Google’s algorithm considers more than 200 factors when ranking a website, but none of them matter if your pages are missing from its index.
Crawlability and indexation form the foundation of SEO because without them, your content can’t appear in search results or reach your audience.
This section outlines how to identify the barriers that stop search engines from accessing and indexing your pages.
1. Determine Indexation Issues
If a page isn’t indexed, it will never rank no matter how strong its content or optimization may be.
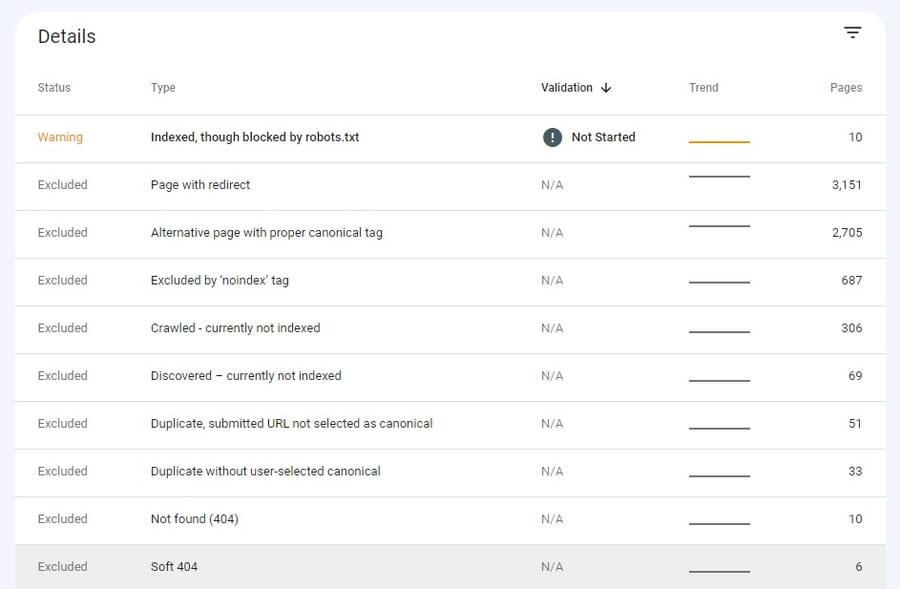
Start by reviewing Google Search Console’s Coverage report to see which pages are indexed, which have warnings and which are excluded.
The report also highlights why certain pages are missing from the index.
Identifying these technical SEO issues early prevents content from disappearing from search results and ensures that new or updated pages are discovered efficiently.
2. Fix Broken Internal Links And Redirect Chains
Internal links help users and search engines move efficiently through your website, but broken links and redirect issues disrupt that flow and create unnecessary friction.
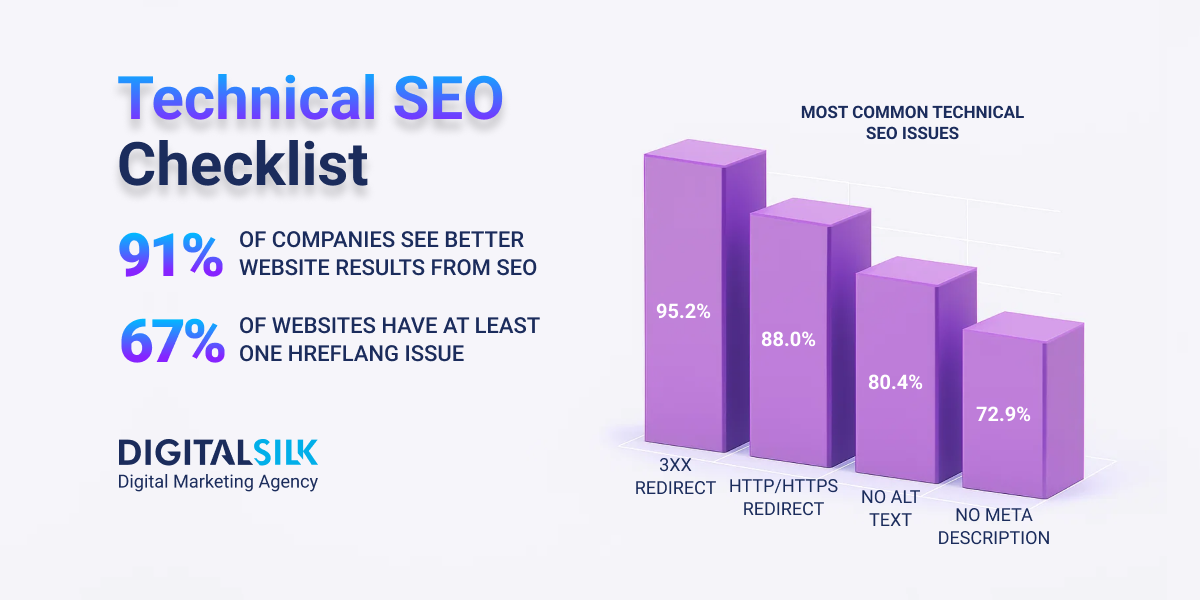
95.2% of websites have 3XX redirect issues, which shows how common these problems are in technical SEO audits.
Start by fixing broken internal links:
- Run a site audit with tools like Screaming Frog to identify broken internal links that point to non-existent pages.
- Review the internal linking report and filter for errors related to broken links.
- Check each broken link to confirm whether the destination page was deleted, moved or linked incorrectly.
- Update the link to point to a live, relevant page or remove it entirely if the page no longer exists
Next, you should resolve redirect chains and loops:
- Search the audit results for redirect chain and redirect loop issues.
- For redirect chains, replace the links so they point directly to the final destination page rather than passing through multiple redirects.
- For redirect loops, adjust the faulty redirects so each one leads to a correct, single destination without circling back.
Addressing these problems allows search engines to crawl your site more efficiently and helps users reach the right content without unnecessary delays.
3. Robots.txt Issues
The robots.txt file tells search engines which pages they should or should not crawl.
This helps direct crawlers toward your most valuable pages and prevents them from wasting time on low-priority areas like admin dashboards or login pages.
When this file is misconfigured, search engines may miss important pages entirely, reducing your visibility in search results.
A well-structured robots.txt file might look like this:
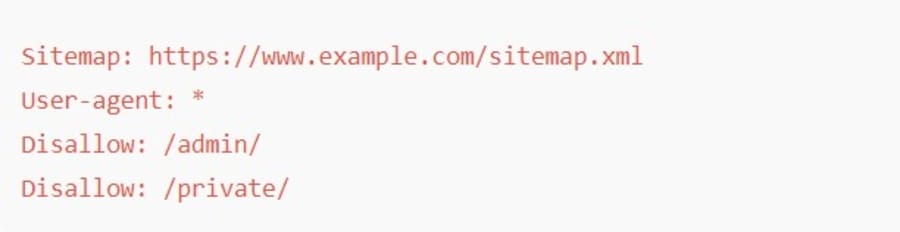
In this example, search engines are guided to your sitemap and blocked from crawling sensitive or irrelevant sections of the site.
Keep in mind that blocking a page in robots.txt prevents crawling but doesn’t guarantee the page stays hidden from search results.
Sensitive content should also be protected through other methods, like password protection.
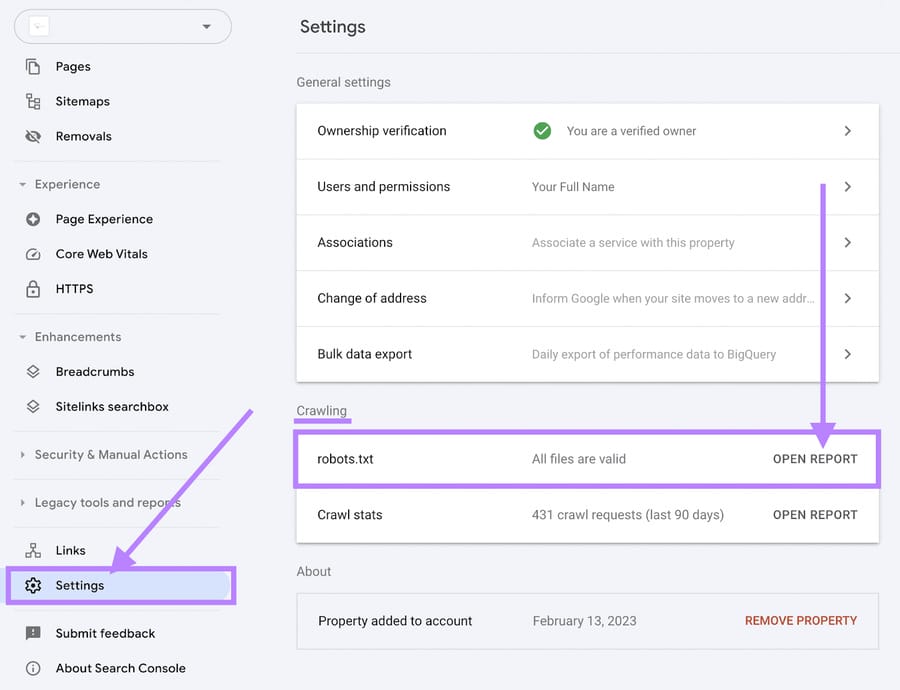
If your site doesn’t have a robots.txt file, create one using a generator tool or CMS plugin. Then, add your sitemap URL to help search engines discover your key pages efficiently.
Regularly review your robots.txt file in Google Search Console under the Crawling settings to check for errors or warnings.
4. Check Robots Meta Tags
Robots meta tags tell search engines what they should or should not do with a specific page.
Placed in the <head> section of the page, they guide whether a page is indexed in search results and whether search engines should follow its links.
Here are some common examples:
- <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”> — Tells search engines not to index the page.
- <meta name=”robots” content=”nofollow”> — Tells search engines not to follow links on the page.
- <meta name=”robots” content=”noarchive”> — Prevents search engines from storing a cached version of the page.
- <meta name=”robots” content=”nosnippet”> — Prevents search engines from showing a text snippet or video preview in search results.
- <meta name=”robots” content=”noimageindex”> — Prevents search engines from indexing any images on the page, but the page itself can still be indexed.
- <meta name=”robots” content=”unavailable_after:[date]”> — Tells search engines to deindex a page after a specific date/time. Example: <meta name=”robots” content=”unavailable_after: 2025-12-31T23:59:59″>
For most websites, you don’t need to add these tags unless you have a specific reason.
By default, search engines will index the page and follow its links, which is what you want for pages you intend to rank.
Use noindex for pages that add no value in search, such as admin areas, staging environments, duplicate content variations or temporary pages for product launches and promotions.
Audit these tags regularly, because adding them to the wrong pages can remove valuable content from your search visibility.
5. Manage AI Access With An LLM.txt File
As generative AI tools continue expanding their data collection, SEO strategies now extend beyond search engines to managing how Large Language Models (LLMs) interact with your content.
This is no longer a theoretical concern, as LLMs are indexing and referencing brand content in ways that impact visibility, attribution and server efficiency.
An llm.txt file is a proposed standard, modeled after robots.txt, that lets you define which AI crawlers can access your site for model training.
In technical SEO, LLM text refers to content structured for both human audiences and AI systems.
This includes clear headings, consistent terminology and contextual clarity so that LLMs can process and represent your brand accurately.
The llm.txt file complements this by defining the boundaries of that interaction.
Here’s how to approach it:
- Define AI access rules with an llm.txt file placed at the root of your domain (e.g., yoursite.com/llm.txt)
- Use a LLM Text Generator tool to toggle permissions for common AI crawlers like GPTBot, ClaudeBot and others, with the default setting allowing access
- Restrict access to specific user-agents if your content is proprietary, sensitive or unsupported for open reuse
This technical SEO strategy helps you:
- Protect proprietary assets from being used to train commercial AI models without permission
- Reduce server load from aggressive crawler behavior that can degrade performance
- Preserve control over how your brand and expertise are interpreted by AI tools
6. Ensure JavaScript SEO Compatibility
JavaScript-heavy websites often run into SEO visibility issues because Googlebot may struggle to fully render or index dynamic content.
Here’s how to check and fix that:
- Test rendering and indexing: Use the Mobile-Friendly Test and URL Inspection tool in Search Console to see if Google is rendering your JS content. Check for missing text or functionality in the “Rendered HTML.”
- Consider pre-rendering or server-side rendering (SSR): If your content isn’t fully visible, you can use dynamic rendering tools like Prerender.io or shift to SSR via Next.js as the preferred framework, or its Nuxt.js alternative.
- Audit JavaScript performance: Heavy JS can impact Core Web Vitals. Tools like Lighthouse or WebPageTest show how long it takes scripts to execute and if they block rendering.
- Monitor Googlebot crawl behavior: Analyze server logs to ensure Googlebot is actually requesting JS resources. If not, it may not be processing your content at all.
Poor JavaScript SEO equals invisible content, so always ensure critical elements like product info, pricing or calls-to-action (CTAs) don’t rely entirely on JS.
7. Validate XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap gives search engines a clear list of your most important pages and helps them crawl and index your site efficiently.
Without it, crawlers rely entirely on internal links to discover content, which means key pages such as your technical SEO consultants or service pages may be missed.
If the file includes broken URLs or misses important sections, crawl resources are spent on the wrong pages while your priority content stays undiscovered.
Most CMS platforms like WordPress, Shopify and Wix generate this file automatically. You can usually find it at yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml or, for larger sites, at yourdomain.com/sitemap_index.xml.
Even when a CMS generates this file, it still needs to be reviewed regularly to reflect your actual site structure.
A standard XML sitemap uses these tags:
- <urlset> defines the structure of the file
- <url> contains each page entry
- <loc> specifies the page’s full URL
- <lastmod> shows the last updated date of the page
- <changefreq> suggests how frequently the page may change (optional)
- <priority> indicates how important the page is relative to others (optional)
Here is an example sitemap for a hypothetical technical SEO company:

To submit your sitemap to Google:
- Open Google Search Console
- Go to the Sitemaps section in the menu
- Enter the full URL of your sitemap
- Click Submit
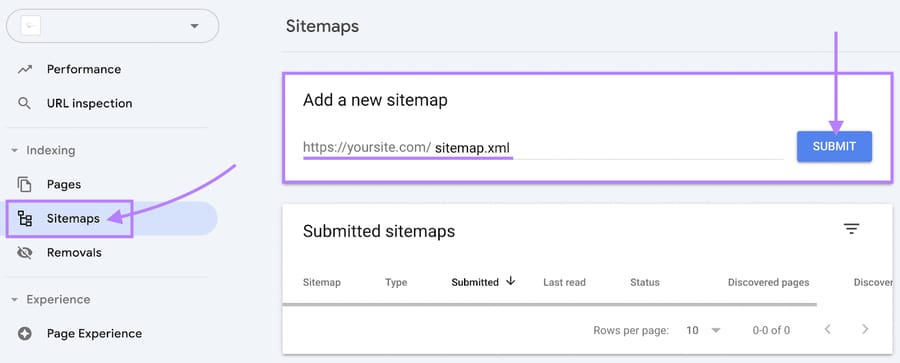
This ensures your technical SEO service and other high-priority pages are easy for search engines to find and index correctly.
Step 4. Analyze Technical On-Page Elements
On-page elements like page titles and meta descriptions are the first signals search engines and users see.
If they’re missing or poorly written, you lose control over how your pages appear in search results and reduce your chances of getting the click.
When two competing pages meet the same search intent, these small technical details can influence which one earns the traffic.
1. Review Page Title Tags
Title tags help Google understand what your page covers and decide how to display it in search results.
92.6% of top-ranking pages include a title tag, and when one is missing, Google replaces it with the h1 heading or rewrites it entirely.
In both cases, the message shown in search may not reflect your goals.
At Digital Silk, we write title tags that are clear, focused and aligned with what our audience is searching for.
This ensures our key pages appear in search with the message we intend.
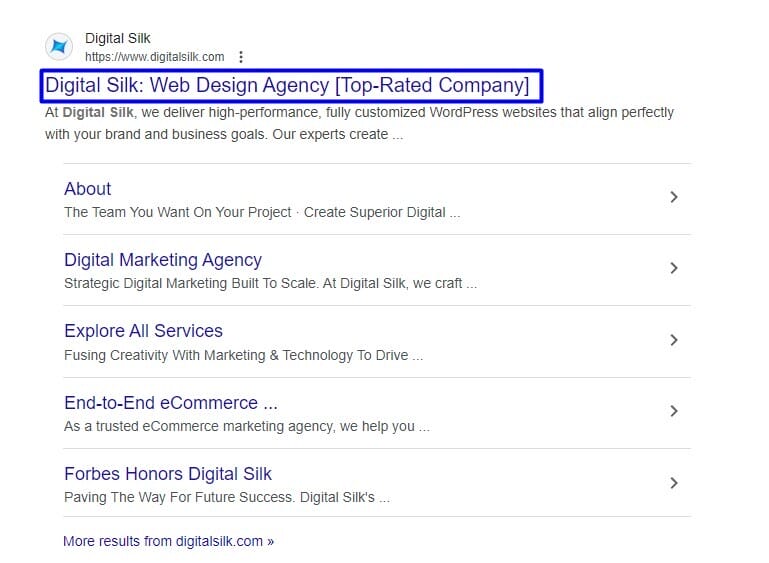
Each page should have a unique title tag that:
- Clearly describes the content of the page without overloading it with keywords
- Follows a consistent, readable format across your site
- Stays under 60 characters, so it’s displayed fully in search
Leaving these out forces Google to make assumptions about what matters on your page.
2. Rewrite Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions appear below your page titles in search and help persuade users to click.
Google rewrites them 60–70% of the time, but a clear and relevant description improves the chance that the right message shows up.
For example, the meta description on our digital marketing page explains our approach and what clients can expect, helping guide the click from search results to our site.
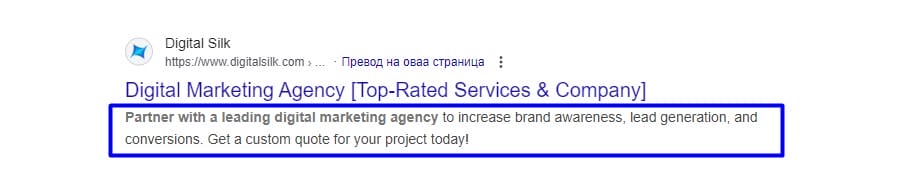
Prioritize writing meta descriptions for your most important pages and focus on:
- Explaining what the user will gain from visiting the page
- Writing in natural language rather than stuffing keywords
- Keeping descriptions complete but short enough to display properly
Audit your site for missing, duplicated or outdated descriptions to avoid missed opportunities in search results. Even when Google rewrites them, your draft guides what users see.
3. Add Canonical Tags
Canonical tags help search engines identify which version of a page should be indexed when multiple variations exist.
Without clear canonicals, ranking signals are split across duplicate URLs, which weakens visibility and creates confusion for search engines.
A strong canonical strategy keeps indexing aligned with your priorities and helps search engines focus on the pages that matter most.
To apply them correctly:
- Always use full URLs, including https://, to remove ambiguity
- Place canonical tags in the <head> section where search engines expect to find them
- Point directly to the preferred version, without creating chains across multiple URLs
- Use self-referencing canonicals on your main pages to confirm their authority
- Make sure your internal links, sitemaps and redirects consistently point to the canonical version
Example of a canonical setup:
- Preferred URL: https://example.com/services/web-design
- Variant URL: https://example.com/services/web-design/?ref=summer-campaign
- Canonical tag should point to: https://example.com/services/web-design
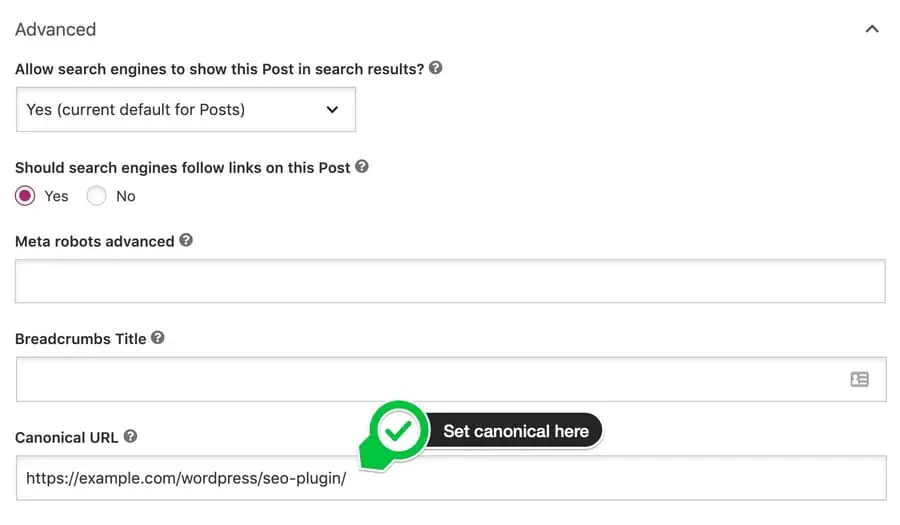
In WordPress, plugins like Yoast SEO or RankMath allow you to define canonical tags directly in the page settings so the correct version is always specified.
The plugins normally handle the canonical element automatically, but if you want to set a different one, you can do so manually.
4. Implement Hreflang For International SEO
Hreflang tags tell search engines which language and regional version of a page should appear for users in different countries.
For global brands, this prevents the wrong version of a page from showing up in search results, giving users content in the language and format they expect.
67% of websites have at least one hreflang issue, and the most common problem is a missing x-default tag, which signals to search engines what version to show when no other language or region matches the user’s settings.
For instance, Airbnb uses hreflang tags across country-specific and language-specific pages so that a traveler in France sees the French version of the site, while a visitor in the US sees the English version, all without confusion in search results.
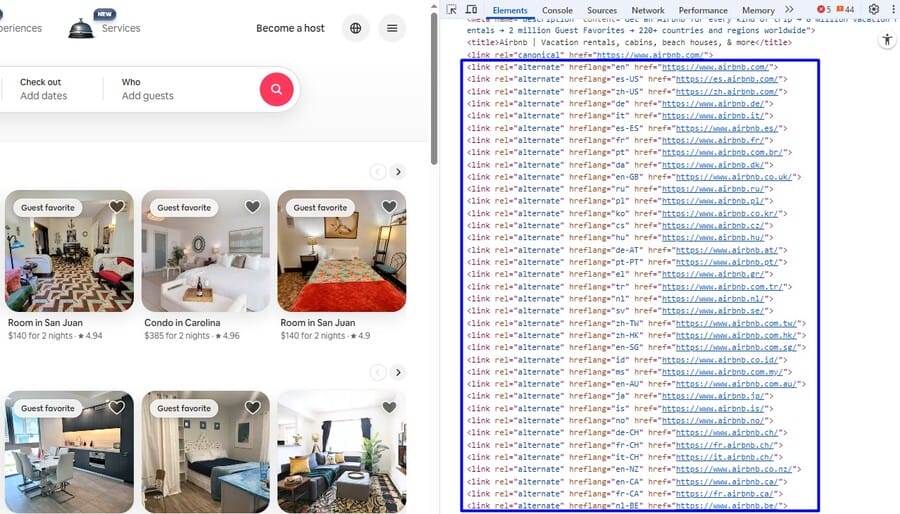
Well-implemented technical SEO solutions for hreflang setup look like this:
- Each language and regional version of a page has a hreflang tag pointing to itself and to the other variations.
- An x-default tag is included to serve as a fallback when no specific language or region applies.
- All hreflang tags are placed in the <head> section of the HTML or included in the sitemap to ensure they are recognized.
- Language and region codes follow the correct ISO standards to avoid errors.
International SEO requires significant effort, from translations to technical implementation, but it helps deliver a better experience for users who expect content in their own language and format.
5. Add Structured Data
Structured data helps search engines interpret the context of your pages, whether that’s information about your products, your organization or the content’s authorship.
This improves how your pages appear in search and supports Google’s understanding of your expertise and credibility.
40% of SEO teams still manage structured data manually, which can give them more control over how they structure important data points, but limits how efficiently they scale that work across large sites.
Today, JSON-LD is the preferred format for structured data because it keeps the code separate from your HTML and is easier to manage. Older formats like Microdata and RDFa still exist but are rarely necessary for modern implementations.
To implement structured data efficiently, you should:
- Select schema types that align with your business goals. For most websites, Product, FAQ, How-To, Organization and Local Business schema are the most relevant.
- Apply schema at the template level so it scales automatically across your site, instead of adding it manually to each page.
- Validate your markup before publishing using Google’s Rich Results Test or Schema Markup Validator to prevent errors.
- Monitor structured data in Google Search Console to catch any indexing or performance issues early.
Here is an example schema markup for a technical SEO company that improves how your technical SEO page appears in search results and supports trust-building rich snippets.

Focus on how your structured data integrates with the rest of your technical SEO.
If your company operates from a specific location, you can implement local business schema to signal that geographic relevance to search engines.
This helps Google understand where your services are available and improves visibility in local results like the map pack and region-specific queries.
It also strengthens consistency across your technical SEO setup, aligning structured data with your site’s content and metadata.
Here’s an example of a schema markup for a local business in Los Angeles, California:

Make sure your hreflang, canonical tags and structured data aren’t sending mixed signals about the page’s purpose.
Step 5. Prioritize Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals measure how your website performs in real-world conditions where speed, stability and responsiveness directly shape user behavior and search visibility.
70% of consumers say that page speed influences their purchasing decisions, so improving these metrics has a clear impact on revenue and growth.
Your teams should focus on the three metrics that matter most:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures how long it takes for the largest visible element, such as a hero image or main content block, to load fully.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Tracks unexpected shifts in layout during load, like buttons or images moving without warning, which frustrate users and cause accidental clicks.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Measures how quickly the site responds when a user clicks, taps or types, reflecting the real responsiveness of the experience.
In 2025, only 52.7% of websites meet Google’s Core Web Vitals benchmarks, showing that technical performance is still a common weakness across industries.
Performance audits reveal what’s slowing down your site, whether it’s oversized media files, inefficient scripts or server delays that affect load times and responsiveness.
Step 6. Focus On Accessibility & Security
A user-friendly website meets the needs of both users and search engines. Accessibility removes barriers for users, while website security protects user data.
Together, they improve page experience and help your technical SEO checklist drive stronger search visibility and engagement.
1. Use HTTPS Connections
Secure data transfer is a baseline expectation for modern websites.
88.1% of websites now run on HTTPS by default, protecting user data as it moves between the browser and your server.
If your technical SEO audit service finds that HTTPS is missing or misconfigured, it should be prioritized.
To implement this strategy correctly:
- Acquire and install an SSL certificate, typically available through your hosting provider.
- Check your site by clicking the padlock icon next to the domain and confirming it shows “Connection is secure.”
- Audit for mixed content, where HTTPS pages load resources like images or videos over insecure HTTP links. This weakens the connection and may block parts of the page from displaying correctly.
Mixed content creates security risks and may interfere with monetization features such as display ads, while also reducing user trust.
2. Optimize Image Sizes
Large, unoptimized images slow down your website and degrade the user experience.
Smaller or compressed image files load faster, improving page speed and reducing bounce rates.
Key actions to take:
- Compress image files before uploading. Tools like TinyPNG or built-in CMS compression options help reduce file size without losing visible quality.
- Use modern image formats. WebP lossless images are 26% smaller than PNGs, and WebP lossy images are 25–34% smaller than JPEGs. These formats deliver faster load times without sacrificing clarity.
- Deliver images through a Content Delivery Network (CDN), which stores copies on servers closer to your users’ locations.
- Enable responsive image scaling so your site serves images sized appropriately for each device, avoiding oversized downloads on mobile.
3. Add Alt Tags
Alt text describes what an image shows, so it’s inherently more accessible to users who rely on screen readers.
55.5% of websites have missing alt tags, which means they overlook a simple way to improve both accessibility and SEO.
From a technical SEO solutions perspective, alt tags help search engines understand image content, improve image search visibility and support page relevance.
Your teams should:
- Write descriptive alt text for all images, not just decorative ones.
- Use clear, meaningful language that describes what the image contains, rather than stuffing keywords.
- Include alt text wherever images also serve as links, since it functions like anchor text in those cases.
Optimizing for accessibility and security helps your technical SEO solutions drive better visibility while creating a smoother experience for every user.
Step 7. Check External Links
External links connect your pages to reputable sources on other domains.
They help search engines understand the context of your content and show users that your information is backed by credible data.
A strong external linking strategy improves trust and adds depth to your content.
At least 66.5% of backlinks eventually break, while in 47.7% of cases, the page they point to is removed entirely.
Broken external links harm the user experience and weaken how your content is interpreted by search engines.
A technical SEO service should flag these issues early, so they can be addressed before they impact performance.
Key actions to prioritize:
- Audit outbound links regularly and replace or remove any that lead to 404 errors or removed pages.
- Focus on indexable pages, where broken links hurt both user trust and search visibility.
- Add links to authoritative sources when they help support your content and provide additional context.
Also, avoid creating dead ends on your own site. Every indexable page should link to other useful content or trusted external resources, so users and search engines always have a clear path forward.
Address Technical SEO Issues With Digital Silk
Technical SEO is where your website’s performance is shaped long before content or campaigns go live.
Solving crawl issues, indexation gaps and page speed problems is what makes search visibility sustainable.
Digital Silk‘s experienced technical SEO consultants work directly with your teams to audit complex site structures, implement scalable fixes and align your technical priorities with measurable business outcomes.
As a professional digital marketing agency, our services include:
- SEO services
- Social media marketing
- Paid advertising
- Custom web design
- Custom web development
- Branding solutions
Our team leads every project with proactive planning and clear communication to achieve measurable results.
Contact our team, call us at (800) 206-9413 or fill in the Request a Quote form below to schedule a consultation.
"*" indicates required fields